The Ultimate EV Charging Guide for Electric Vehicle Owners
Navigate the world of electric vehicle charging with our ultimate EV charging guide. Learn about different charging levels, home vs. public charging, and how to optimize your EV charging experience.
Greenlogic
Table of Contents
Introduction
As we collectively steer towards a more sustainable future, the prominence of electric vehicles (EVs) is on the rise, making EV charging an increasingly essential aspect of our daily lives. With this shift in transportation preferences, EV owners must grasp the nuances of EV charging. This all-inclusive EV charging guide aims to arm you with essential knowledge and practical advice to effortlessly navigate the realm of EV charging.
Decoding EV Charging: The Fundamentals
Before we dive into the specifics of home and on-the-go charging in this EV Charging Guide, let’s first decode the fundamentals of EV charging.
EV charging stations primarily come in three forms:
- Level 1 (L1)
- Level 2 (L2)
- DC fast charging (DCFC)
Level 1 Charging, the most basic form of EV charging, utilizes a standard 120-volt AC outlet. Although it’s the slowest method, it’s also the most accessible, requiring no special equipment beyond the charging cord that comes with most EVs.
Understanding the different types of EV charging might seem like learning a new language at first. But don’t worry, it’s not that hard. Think of Level 1 Charging like a leisurely walk. It’s not the quickest way to get to your destination, but it’s reliable and gets the job done. This method is perfect for overnight charging or if you’re just topping up your battery during a workday.
Level 2 Charging employs a 240-volt AC outlet, similar to those used by large appliances like ovens and dryers. It’s considerably faster than Level 1 and is the most prevalent type of EV charging station you’ll encounter in public. You can learn more about Level 2 charging.
Consider Level 2 Charging as a brisk jog. It’s quicker and more efficient. This is the most common type of EV charging and can fully charge most EVs within a few hours.
DC Fast Charging, as the name suggests, is the quickest method. These high-powered stations can charge most EVs to 80% in about 30 minutes. However, not all EVs can handle this level of power, and frequent fast charging can potentially shorten battery life.
DC Fast Charging is the sprinter of the group. It’s the fastest way to charge your EV, often up to 80% in just 30 minutes. However, just like sprinting, it’s not something you should do continuously. Frequent fast charging can potentially shorten battery life, so it’s best used sparingly for long trips.
Grasping these types of charging and their implications is key to alleviating ‘range anxiety’ – the fear that your EV won’t have enough charge to reach your destination.

AC vs. DC Charging: The Power Behind the Charge
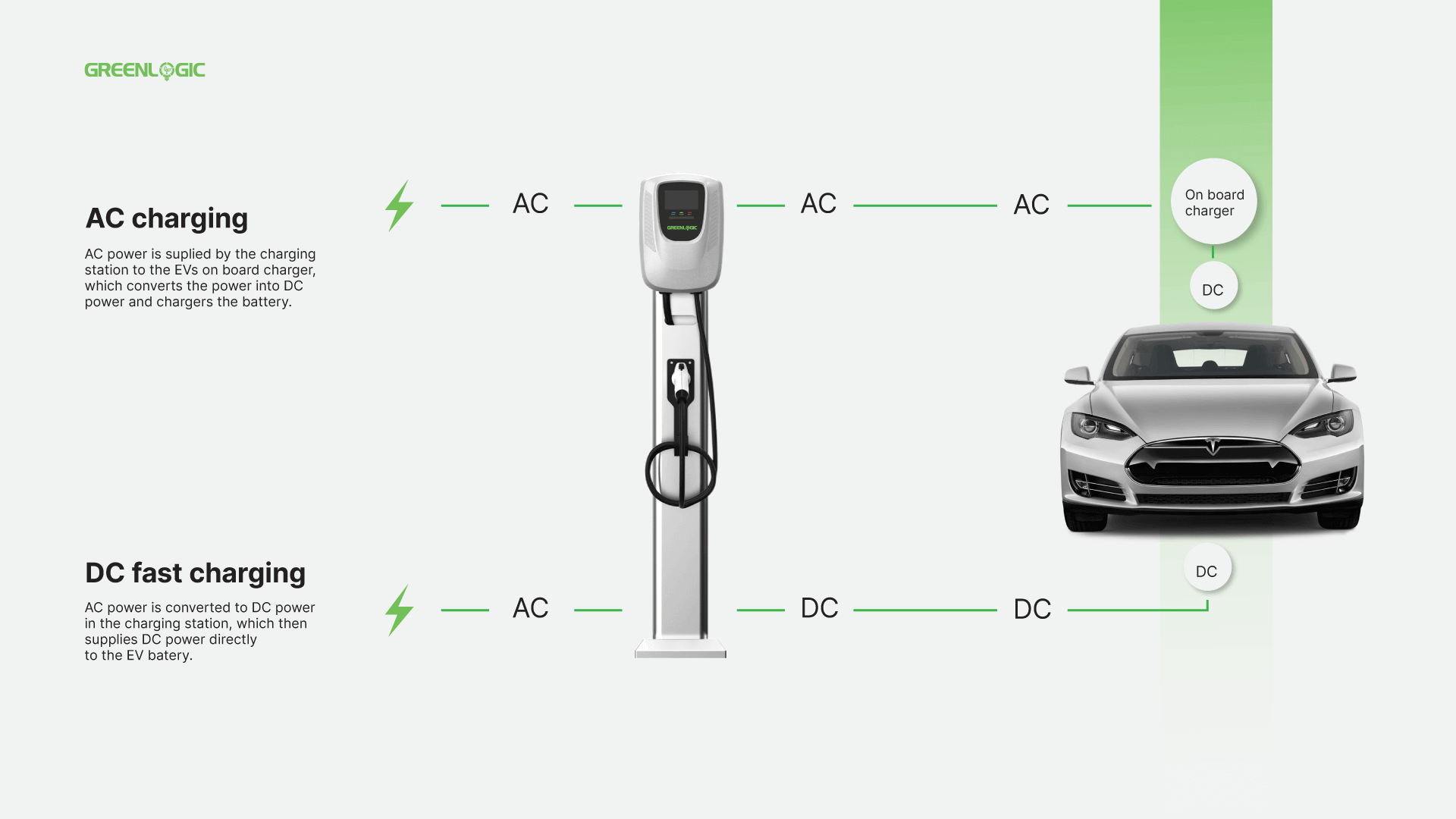
AC, or Alternating Current, is the type of electricity that comes from your home or office outlets. DC, or Direct Current, is the type of electricity stored in your EV’s battery.
When you use a Level 1 or Level 2 charger, the AC electricity from the outlet is converted to DC by the vehicle’s onboard charger. This process, while reliable, is time-consuming. On the other hand, DC Fast Charging stations convert AC to DC within the charger itself, resulting in faster power delivery directly to the EV battery.
Powering Your EV at Home
Powering your EV at home is convenient and the most cost-effective way to keep your vehicle charged. Let’s dissect the two types of chargers you can install at home.
Level 1 Home Charging is the simplest method. All you need is a standard electrical outlet. While it’s slow (charging a fully depleted battery can take 8-20 hours, depending on the vehicle), it’s perfectly adequate if you drive less than 40 miles per day or can leave your car plugged in overnight.
Level 1 Home Charging is as straightforward as charging your smartphone. All you need is a standard electrical outlet. It’s slow but dependable. If your daily commute is short or you can leave your car plugged in overnight, Level 1 charging is a cost-effective solution.
Level 2 Home Charging requires a bit more setup. You’ll need to install a 240-volt outlet and a charging station. But the payoff is worth it. You’ll wake up every morning with a fully charged EV, ready to tackle the day. It charges much faster than Level 1, typically fully charging an EV in 4-6 hours.
When setting up home charging, consider your daily driving habits, available electrical infrastructure, and budget. And remember, smart charging during off-peak electricity hours can help you save on your energy bill.

Decoding EV Charging Stations
EV charging stations are more than just power outlets. They’re sophisticated devices that communicate with your EV to ensure safe and efficient charging. They come in various shapes and sizes, from small wall-mounted units for home use to large freestanding stations for public use. Some have additional features like WiFi connectivity for remote monitoring and control.
With different types of charging stations, comes different level of power (kW) they can output. The most common types include:
- Level 1 Charging Stations: These stations provide between 1 and 1.8 kWh of power through a standard 120-volt AC outlet. While they are the slowest option, they are also the most accessible, as they can be used with any standard electrical outlet.
- Level 2 Charging Stations: These stations offer a significant speed boost compared to Level 1 stations. They provide between 3.3 and 19.2 kWh of power through a 240-volt AC outlet, which is commonly found in residential garages. Level 2 stations are often used for home and public charging, and they can fully charge an EV battery in just a few hours.
- DC Fast Charging Stations: These are the fastest charging stations available. They convert AC power to DC power within the station itself and deliver it directly to the battery, significantly speeding up the charging process. DC Fast Charging stations can provide power output ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW, depending on the station and the vehicle’s capabilities. They can charge a battery to 80% in just 20 minutes to 1 hour.
At Greenlogic, we offer a range of charging solutions to meet your business needs.
Our flagship charger, the EVC 10, 48A, is designed to handle the most powerful EV batteries. It delivers unparalleled charging speed, allowing you to power up your electric vehicle faster than ever before. With its SAE J1772 compliant, type 1 plug and adjustable power settings, you can easily tailor the charging process to suit your vehicle’s needs. From 80A down to 16A, the EVC10 has you covered.
Our charging stations are not just about power; they’re also about convenience and control. With LAN connectivity and optional Wi-Fi or 4G support, you can monitor and control your charging sessions remotely. Plus, with OCPP 1.6J compatibility, the EVC10 seamlessly connects your EV charger to the cloud, opening up a world of possibilities. Monitor charging data, track usage, and integrate with smart energy management systems to optimize your charging experience.
But we don’t stop at providing top-tier charging stations. We also offer a comprehensive EV charging management platform that allows you to oversee charging activities, manage assets, and keep track of user interactions, all from a single dashboard. Monitor financials, tailor subscription plans, and leverage analytics to optimize operations.
For EV drivers, we offer the Greenlogic EVC App, which provides power and convenience right in your pocket. With our app, you can locate charging stations, start and stop charging sessions, view your charging history, and manage your payment method and account settings, all from your phone.


Investing in EV charging stations is not just about meeting a growing demand; it’s also about reaping significant benefits. By offering EV charging, you can boost your property value, delight your residents, unlock new revenue streams, lead in sustainability, secure your future, and attract sustainable customers.
EV Charging Connector Types
Different levels of EV charging use different types of connectors. The J1772 (Type 1) connector is used in North America for Level 1 and Level 2 charging. For Level 3 EV charging, connectors like the CCS (Combine Charging System), CHAdeMO, and Tesla Superchargers (NACS) are used. Understanding these connectors can help you better navigate the world of EV charging.

The Economics of EV Charging
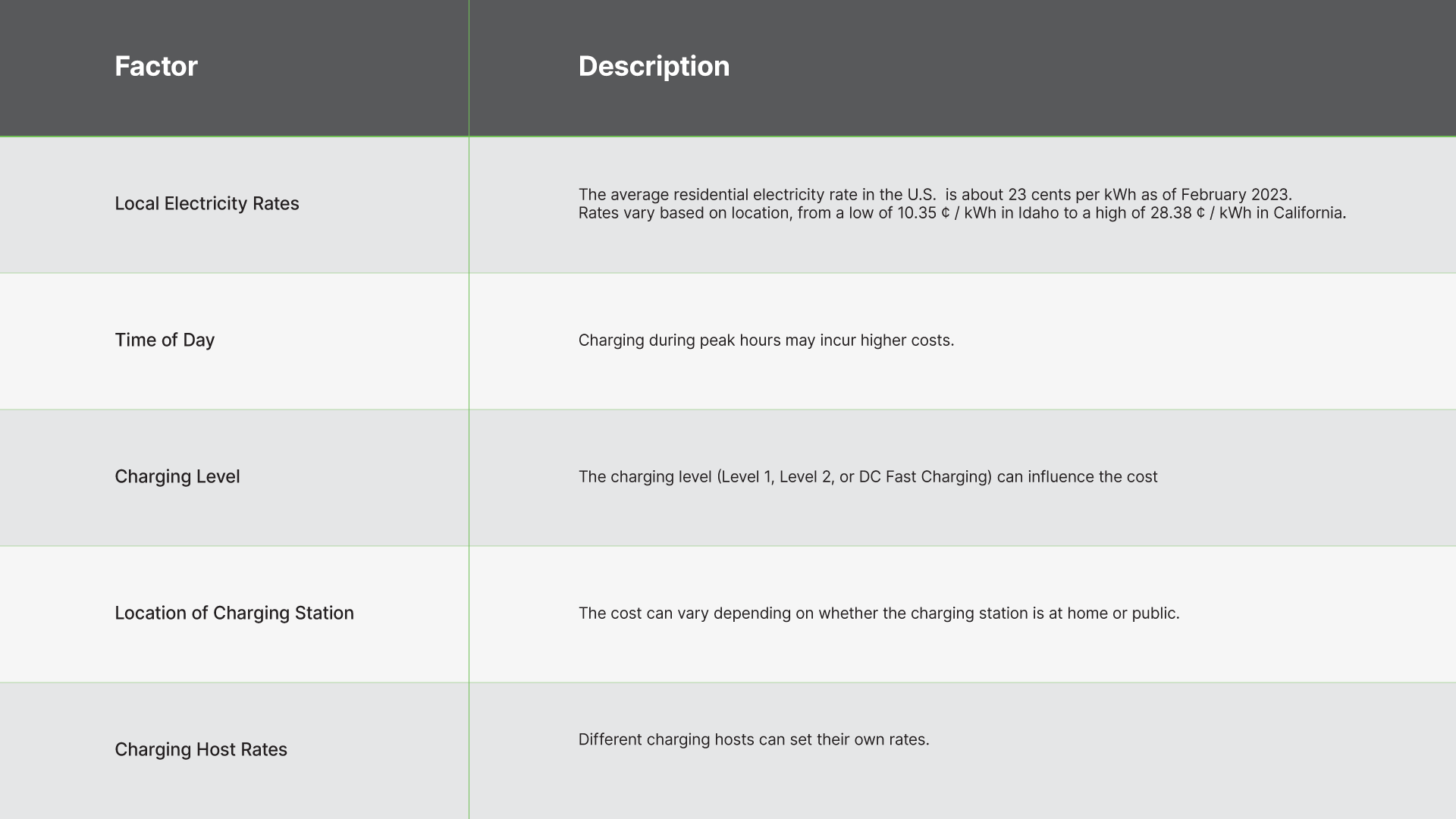
The cost of charging an electric vehicle (EV) can vary significantly, influenced by several factors. These include your local electricity rates, the time of day (peak hours may incur higher costs), the charging level (Level 1, Level 2, or DC Fast Charging), and the location of the charging station (home or public). Despite these variables, it’s important to note that, on average, charging an EV tends to be more cost-effective than refueling a conventional gas-powered vehicle.
As of February 2023, the average residential electricity rate in the U.S. is about 23 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Bear in mind that the electricity rate will vary widely based on where you live. For instance, rates vary from a low of 10.35 ¢ / kWh in Idaho to a high of 28.38 ¢ / kWh in California.
When it comes to EV charging, different charging hosts can set their rates. This is where an EV charging app can come in handy. With an app like the Greenlogic EVC App, users can check the pricing and availability of charging stations in real time. This allows EV drivers to plan their charging sessions effectively and potentially save on costs.
In addition to providing information on charging station pricing and availability, the Greenlogic EVC App also offers features like map-based station navigation, real-time station availability, instant charging start, a convenient reservation system, and a comprehensive charging history. This makes it a valuable tool for EV drivers looking to manage their charging costs and sessions efficiently.
Charging Your EV On-the-Go
While home charging covers most of your needs, there will be times when you’ll need to charge on the go. Thankfully, public EV charging stations, like those offered by Greenlogic, are becoming increasingly common.
Level 2 Public Charging stations are widely available in places like shopping centers, parking garages, and even some street parking areas. Charging times are similar to Level 2 home charging, making them a convenient option for topping up your battery while you shop or work.
DC Fast Charging stations are typically found along major highways and in commercial areas. They’re designed for long-distance travel, allowing you to recharge most of the battery in a short coffee break.
Using public charging stations usually involves a payment, either through a subscription service or a pay-as-you-go method. Many charging networks, including Greenlogic, offer mobile apps to find nearby stations, check their availability, and handle payment.

How to Optimize Your EV Charging Experience
Now that you’re familiar with the basics of EV charging, here are some tips to optimize your experience:
Preserve Battery Life: Avoid letting your battery level drop too low or charging it to 100% too often. Most manufacturers recommend keeping the battery level between 20% and 80% to prolong its life.
Optimize Charging Speeds: While fast charging is convenient, slower charging methods are gentler on your battery. Whenever possible, use Level 2 or Level 1 charging.
Maintain Your Battery: Regular maintenance of your EV battery can help prolong its life. This includes keeping it clean and ensuring it’s not exposed to extreme temperatures.
Understand Your EV’s Charging Capabilities: Different EVs have different charging capabilities. Understanding your vehicle’s specific capabilities can help you choose the right charger and optimize your charging sessions.
- Harness Technology: Numerous apps and tools, like the Greenlogic app, can enhance your EV charging experience. From finding the nearest charging station to scheduling charging during off-peak hours, these resources can make owning an EV even more convenient.
The Future of EV Charging
The world of EV charging is evolving rapidly. Innovations like wireless charging, ultra-fast charging, and V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) technology are on the horizon. As the EV market continues to grow, we can expect to see continued advancements in charging technology, making EV ownership even more convenient and enjoyable.
Conclusion
Now that you’re equipped with the essential knowledge about EV charging, you’re ready to make the most of your electric vehicle. Remember, as we continue to drive towards a more sustainable future, your journey with your EV is just beginning. So plug in, charge up, and enjoy the ride with Greenlogic. Want to learn more about our EV charging solutions? Visit our webpage or contact us today, and don’t forget to share this EV charging guide with your fellow EV owners and enthusiasts!
FAQ
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle?
The time it takes to charge an electric vehicle can vary greatly depending on the type of charger used and the specific vehicle model. With Level 1 Home Charging, charging a fully depleted battery can take between 8-20 hours. On the other hand, Level 2 Home Charging, which requires a special 240-volt outlet and charging station, can typically fully charge an EV in 4-6 hours. Finally, DC Fast Charging can charge most EVs to 80% in about 30 minutes.
How much does it cost to charge an EV at home vs. at a public charging station?
The cost of charging an EV can be influenced by several factors including local electricity rates, the time of day, and the type of charging station. As of February 2023, the average residential electricity rate in the U.S. is about 23 cents per kilowatt-hour. However, these rates can vary based on location. The cost of public charging can vary widely, as charging hosts can set their own rates. Users can check the pricing and availability of charging stations in real time using the Greenlogic EVC App.
Can frequent fast charging damage my EV's battery?
Yes, frequent fast charging can potentially shorten the lifespan of your EV’s battery. Fast charging is most effective and least harmful to the battery when it’s used sparingly, such as during long trips. For regular charging, slower methods like Level 2 or Level 1 are recommended, as they are gentler on the battery.
What is the difference between Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging?
Level 1 Charging uses a standard 120-volt AC outlet and is the slowest method, providing between 1 and 1.8 kWh of power. Level 2 Charging, on the other hand, uses a 240-volt AC outlet and provides significantly faster charging speeds, delivering between 3.3 and 19.2 kWh of power. DC Fast Charging is the fastest method, capable of delivering power outputs ranging from 50 kW to over 350 kW. It is used less frequently due to potential battery wear but is useful for long-distance travel.
How can I find public EV charging stations near me?
The Greenlogic EVC App is a great tool for locating charging stations near you. It provides real-time station availability, allows you to start and stop charging sessions, view your charging history, and manage your payment method and account settings. Additionally, other apps and websites like PlugShare and ChargePoint can also help you find public charging stations.
Should I charge my EV to 80% or 100%?
While it’s generally safe to charge your EV to 100%, many experts recommend charging only up to 80% for daily use. This is because constantly charging to 100% can put stress on the battery and potentially shorten its lifespan. However, if you’re planning a long trip and need the extra range, charging to 100% occasionally is fine.
What is the best charging routine for EV?
The best charging routine for your EV depends on your daily driving habits and the specific model of your vehicle. However, a common routine is to plug in your EV each night and let it charge to 80% (or 100% if you need the extra range). This ensures your vehicle is ready to go each morning.
Should I buy a Level 1 or Level 2 EV charger?
Whether you should buy a Level 1 or Level 2 EV charger depends on your specific needs. If you drive a lot each day and need to recharge your vehicle quickly, a Level 2 charger may be the best option. However, if you only drive a few miles each day, a Level 1 charger may be sufficient.
Remember to always consider your daily driving habits, the specific model of your vehicle, and the recommendations of your vehicle’s manufacturer when deciding on a charging routine or purchasing a charger.
Tags:
Greenlogic's Newsletter
Get exclusive access to valuable insights, company news, industry trends, cost-saving tips, and practical resources.








